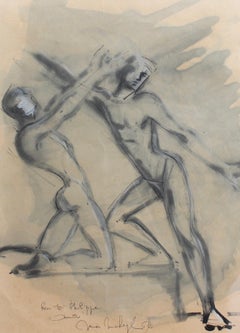Winold Reiss Art
American, 1886-1953
Winold Reiss was a German-American muralist and illustrator who is best remembered for his portraits of the Blackfoot Indian tribe. His work was so revered by the tribe that when he died, his ashes were spread across sacred burial grounds.
to
4
1
5
2
2
Overall Width
to
Overall Height
to
14
1
9
10
3
1
9
7
4
4
3
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
5
5
4
4
4
14
7,738
4,946
2,504
1,373
5
14
Artist: Winold Reiss
Blackfeet Indians, Great Northern Railway 14 prints
By Winold Reiss
Located in Spokane, WA
A group of 14 Blackfeet Indians prints created by the artist Winold Reiss. The Great Northern Railway printed and released these prints in c. 1940. This is for the entire group...
Category
1940s American Realist Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Lithograph
"The Red Silo" Winold Reiss, Rural Regionalist Landscape, Sunny Day on Farm
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Winold Reiss
The Red Silo
Signed lower left
Watercolor on paper
20 x 29 inches
Winold Reiss (1886-1953) was an artist and designer who emigrated to the United States from Germany in 1913. Probably best known as a portraitist, Reiss was a pioneer of modernism and well known for his brilliant work in graphic and interior design. A compassionate man who greatly respected all people as human beings, he believed that his art could help break down racial prejudices. Like his father Fritz Reiss (1857-1915), who was also an artist and who was his son's first teacher, Winold Reiss was artistically moved by diverse cultures. The elder Reiss focused on folk life in Germany while Winold drew substantial inspiration from a range of cultures, particularly Native American, Mexican, and African-American.
As did many young aspiring artists, Winold Reiss studied with the esteemed painter and teacher Franz von Stuck at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Munich, which was at that time a center of the decorative and fine-arts movement. It is not known whether Reiss met E. Martin Hennings...
Category
Mid-20th Century American Realist Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, Watercolor
Long Time River Woman (Blackfoot Maiden)
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Winold Reiss (1886-1953), who scholars increasingly recognize as a pivotal figure in early 20th-century American art, is known for his evocative portraits that capture the spirit and...
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, Mixed Media
Abstract Still Life with Lute
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Pastel on black paper
Category
Early 20th Century Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, Pastel
Indian Man from Mexico
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Indian Man from Mexico is a souvenir of Winold Reiss’s 1920 sketching tour of Mexico. As he traveled, Reiss’s style began to reflect the influence of the aesthetics, color palette, a...
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, Pastel
The Unraveling Secret
By Winold Reiss
Located in Fort Washington, PA
Medium: Pen and Ink on Board
Dimensions: 16.00" x 12.00"
Signature: Signed Lower Right
"Man in prison with two jailers" - Book illustration.
Category
Early 20th Century Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Ink, Board, Pen
The Forest Duel
By Winold Reiss
Located in Fort Washington, PA
Medium: Pen and Ink on Board
Dimensions: 16.00" x 12.00"
Signature: Signed Lower Left
book illustration
Category
Early 20th Century Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Ink, Board, Pen
Rosalee Sondheimer I
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Winold Reiss (1886-1953), who scholars increasingly recognize as a pivotal figure in early 20th-century American art, is known for his evocative portraits that capture the spirit and...
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Pastel, Board
Girl in Decorative Wrap
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Winold Reiss (1886-1953), who scholars increasingly recognize as a pivotal figure in early 20th-century American art, is known for his evocative portraits that capture the spirit and...
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Mixed Media, Board
Woodstock
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Signed (in white gouache, at lower left): Winold Reiss; (with estate stamp, at lower right): Winold /
Reiss
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Ink, India Ink
Portrait of Robert Nathaniel Dett (1882-1943)
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Signed (at lower right): WINOLD/REISS
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Pastel
Japanese Girl
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Signed (at lower right): WINOLD/REISS
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Pastel
Separated Spear Woman in Snake Headress
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Mixed media on Whatman board. Signed (at lower right): WINOLD/REISS
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Mixed Media
Henry Whitford
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Mixed media on Whatman board. Signed (at lower left): WINOLD/REISS
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Mixed Media
Related Items
Modern Dancers
By Mick Micheyl
Located in London, GB
'Modern Dancers', pastel, ink and gouache on fine art paper by French artist, singer and sculptor, Mick Micheyl (1964). Two elegant young men are depicted in a graceful dancing pose, arms outstretched, their lithe bodies so agile and limber. Perhaps one of the dancers was her friend, Philippe, to whom the painting is dedicated on the bottom. The dedication says: 'For you Philippe, all my friendship'. Signed: 'Mick Micheyl'. The work has been newly framed and glazed after having been acquired in the S. of France. It is in fair vintage condition commensurate with age showing minor blemishing on the paper. Upon request a video of the piece can be provided.
Dimensions with Frame:
H 75 cm / 29.5"
W 61 cm / 24"
Dimensions without Frame:
H 56 cm / 22"
W 42 cm / 16.5"
About the Artist: Mick Micheyl (1922 - 2019) was born in Lyon and had a busy and rewarding artistic career as a singer, producer, reviewer, metal sculptor, artist. After having received training at the School of Fine Arts in Lyon she became a painter and decorator in the theatre but then commenced a career in the musical activities of a theatrical troupe. She won the ABC competition in Paris in 1949 with a song, Le Marchand de Poésie, which she composed herself. She then performed in many cabarets: L'Échelle de Jacob, Harlequin and Liberty's. In the 1950s she was one of the most important French cabaret singers of that period. One of her titles, 'Un Gamin de Paris', became one of the French standards and also performed by Yves Montand and Robert Clary...
Category
1960s Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Gouache, Paper, Pastel, Ink
Original Painting New Yorker Mag Cover proposal. Army Wedding American Scene WPA
By Antonio Petruccelli
Located in New York, NY
Original Painting New Yorker Mag Cover proposal. Army Wedding American Scene WPA
Antonio Petruccelli (1907 – 1994)
Army Wedding
New Yorker cover proposal, c. 1939
11 1/2 X 8 inches ...
Category
1930s American Realist Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Gouache, Board
1950s "Purple Head" Mid Century Oil and Pastel Portrait Original Drawing
By Donald Stacy
Located in Arp, TX
Donald Stacy
"Purple Head"
c.1950s
Gouache and oil pastel on paper
13.75" x 17" unframed
Unsigned
Came from artist's estate
Donald Stacy (1925-2008) New Jersey
Studied: Newark School of Fine Art
The Art Students League
Pratt Graphic Arts Center
University of Paris 1953-54
University of Aix-en-Provence 1954-55
Faculty: Art Department of the New School
Museum of Modern Art
School of Visual Arts
Stacy Studio Workshop
Exhibitions: Grand Central Moderns
George Wittenborn
The New School
Print Exhibitions, Chicago
University of Oklahoma
Honolulu Museum
Monclair Museum
Wisconsin State College
Louisiana Art Commission
Philadelphia Print...
Category
Mid-20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, Oil Pastel, Gouache
'The Holy Grail', Last Supper, Egyptian Iconography, Seattle Art Museum, Surreal
By Leo Kenney
Located in Santa Cruz, CA
Signed lower center, 'Leo Kenney' (American, 1925-2001) and dated 1947.
A seminal figure in the second generation of Northwest School artists, Leo Kenney was, like many of his conte...
Category
1940s Surrealist Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, India Ink, Watercolor
'Portrait of a Young Navajo', Native American, Arizona, California Woman artist
By Victoria Creech Stewart
Located in Santa Cruz, CA
Signed lower left 'Creech PSWC' and created circa 1975
A compelling pastel study showing the subject dressed in brightly-colored ceremonial robes and gazing past the viewer. An eleg...
Category
1970s American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Pastel, Archival Paper
Petite danseuse aux cheveux défaits, 1991, original lithograph by Jean Jansem
By Jean Jansem
Located in Les Acacias GE, GE
Jean Jansem (1920-2013)
Petite danseuse aux cheveux défaits, 1991
Lithographie sur papier Arches
Signée en bas à droite et justifiée en bas à droite
66 x 47 cm / 76 x 54 cm
Imprime...
Category
Late 20th Century Expressionist Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Lithograph
PRINCE OF CUPS 1979, Signed Lithograph on Arches, Tarot Card Series
By Salvador Dalí
Located in Union City, NJ
Artist - Salvador Dali (Spanish, 1904-1989)
Title - PRINCE OF CUPS, Tarot Card Series
Publisher - DALART N.V.
Year published - 1979
Medium - Lithograph on Arches Cover 270 gsm. 100% acid free, signed in pencil, inscribed 2/5 PP (Printers Proof) by Salvador Dali on lower print margin, publishers mark "DALART N.V. Copyright 1979" blindstamp embossed on lower left print margin. Fine impression, vivid colors, unframed, in very good condition.
Listed in the Albert Field's OFFICIAL CATALOGUE OF THE GRAPHIC WORKS OF SALVADOR DALI, Reference #79-15.
PRINCE OF CUPS from the Tarot Series 1979, is a surrealist style limited edition lithograph by Salvador Dalí (1904 – 1989) Printed on archival Arches paper, 100% acid free. PRINCE OF CUPS depicts a freely drawn, black line portrait of a young Prince wearing his golden yellow crown, sporting a white ruffle collared shirt, looking slightly sideways posed behind a golden chalice...
Category
1970s Surrealist Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Lithograph
"The Volunteer - Civil War" Historical Portrait, 742/1500
Located in Soquel, CA
Limited edition offset print of the original photorealistic painting, a portrait that portrays a historical reenactment of a civil war volunteer by James Bama...
Category
1980s American Realist Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Ink, Offset, Paper
H 26.5 in W 22 in D 0.13 in
Norman Rockwell Original Lithograph Courting Couple, Date, Hand Signed Americana
By Norman Rockwell
Located in Surfside, FL
Norman Rockwell (1894-1978)
Courting Couple at Midnight (with Cuckoo clock)
1972
Offset lithograph print, collotype)
Hand signed in pencil, numbered H AP 9/10
26 x 21 in. (sight),...
Category
1970s American Realist Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Lithograph, Offset
'After School', Art Deco, Woman Artist, AIC, ASL, Paris, Salon d'Automne, PAFA
By Nura Ulreich
Located in Santa Cruz, CA
Signed lower right, 'Nura' for Nura Woodson Ulreich (American, 1899-1950) and painted circa 1935.
This early twentieth-century painter, lithographer, muralist, author, poet and ill...
Category
1930s Art Deco Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Crayon, Watercolor, Gouache, Illustration Board, Pen, Pencil
African Mama - Vintage Illustration in Ink and Watercolor
By Irene Pattinson
Located in Soquel, CA
African Mama - Vintage Illustration in Ink and Watercolor
A charming illustration, by Irene Pattinson (American, 1909-1999), shows a woman with a...
Category
1950s American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, India Ink, Watercolor, Pen
H 13 in W 10 in D 0.25 in
Abstract Geometric Terracotta Jugs, Mid Century Modern Abstracted Still Life
Located in Soquel, CA
Bold mid century modern abstracted pastel on paper still life of several terra cotta jugs and vessels distilled down to their most basic shapes and ar...
Category
1960s Abstract Geometric Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, Pastel
H 24.25 in W 29.75 in D 1.25 in
Previously Available Items
Natokiochkome (Howling Twice)
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
Winold Reiss (1886-1953), who scholars increasingly recognize as a pivotal figure in early 20th-century American art, is known for his evocative portraits that capture the spirit and...
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Paper, Mixed Media
10% deposit for City of the Future, Panel II
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
French modern art made a dramatic entrance into on America in 1913 at the famous Armory Show in New York City. In that same year, German twentieth-century art also arrived, with no fanfare, in the person of Winold Reiss, who disembarked from the S. S. Imperator on October 29, 1913, at Ellis Island in New York harbor. (The most accessible discussion of Reiss remains Jeffrey C. Stewart, To Color America: Portraits by Winold Reiss, exhib. cat. [Washington, D.C.: National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution, 1989]. A very useful overview of Reiss’s career is contained in “Queen City Heritage: Cincinnati Union Terminal and the Artistry of Winold Reiss,” The Journal of the Cincinnati Historical Society 51 [Summer/Fall 1993]). Reiss was already twenty-seven years old when he came to America, thoroughly educated in a rigorous and inclusive heritage of German art that reflected decades of central European modernism.
Reiss’s father, Fritz Reiss (1857–1914), had trained as a landscape painter and portraitist at the renowned academy in Düsseldorf. Working as an illustrator, and proficient in watercolor as well as oil, Fritz Reiss moved his family, in the 1899, to Freiburg, a small village in southwest Germany near the Black Forest, so that he could paint honest portraits of local peasants. This choice reflected a prevailing spirit of romantic nationalism in the fine arts, architecture, and literature that was expressed in arts and crafts movements across Europe. Two of Fritz Reiss’s sons followed their father into art. Hans became a sculptor, immigrated to Sweden, and eventually joined his brother in America. Winold’s first art teacher was his father. In 1911, Reiss went to Munich where he studied with Franz von Stuck at the Academy of Fine Arts and with Julius Diez at the School of Applied Arts. Von Stuck was an influential art nouveau artist, designer, sculptor, and architect whose graphic style tended toward imaginative symbolism. Diez was master of mural painting who gained renown for his commercial poster designs executed in the Jugendstil manner. While Reiss absorbed stylistic influences from both of these men, perhaps the most lasting lesson was the freedom with which German fine artists crossed genres, working in the fine arts and the applied arts as circumstances warranted, without prejudice to their standing in either field. This permeable boundary, a characteristic of German arts and crafts practice, was also championed by John Ruskin and William Morris, in England. While his European versatility enabled Reiss to support his family in America, it ultimately hampered his full acceptance as a fine artist.
Reiss was proficient in graphics, fabric design, interior decoration, mural and poster art, as well as landscape and portrait painting. When he first arrived in America he established himself across a broad range of these interests, working in illustration, poster design, interior decoration, and as a teacher. His first major interior commission, the Busy Lady Bakery in New York City (Stewart, p. 30 illus.), strongly recalls the design work a decade earlier of Josef Hoffman in Vienna and Charles Rennie Mackintosh in Glasgow. While fellow German immigrants were among Reiss’s first commercial patrons, by 1915 he had been invited to lecture on the German poster at the Art Students League in New York. Anti-German feeling accompanying America’s entry into World War I derailed some of Reiss’s projects, but still, in 1914 and 1915, he designed covers for Scribner’s magazine.
None of this, however, was what had drawn Reiss to America. The story goes that he came to America to live out his childhood fantasies. Like many other German boys, Reiss had been captivated in his youth by tales of the American “wild west” widely circulated in the imaginative fiction of the German author Karl May. Reiss had also read, in translation, the works of James Fennimore Cooper. Numerous explanations can be put forth to explain Reiss’s emigration to America in 1913. The combined reasons must have been compelling enough to leave behind a pregnant wife (she and his son, Tjark, born in December 1913, joined him in America in 1914). These reasons included, no doubt, the war clouds over Europe, the increasing militarism of German society (Reiss’s brother Hans, was a pacifist) and the large number of artists already working in Germany. Still, for Reiss, America meant the Indian.
In January 1920, Reiss realized his dream of traveling west to Indian country. He went with a student to the Blackfoot Reservation in Browning, Montana. Thus began a relationship with Native Americans that lasted all of his life. Reiss produced thirty-six portraits of Blackfoot Indians in the winter of 1920. When he exhibited these in New York in 1920, at the E. F. Hanfstaengl Galleries, they were purchased as a group by Dr. Philip Cole, a native of Montana. In October 1920, Reiss made a sketching trip to Mexico, painting portraits and landscapes. As he traveled, Reiss’s style began to reflect the influence of the aesthetics, color palette, and patterns of indigenous American visual culture. He blended this into his now hyphenated German-American vocabulary, reaching for an artistic language expressed in the most universally accessible terms that would convey the respect he felt for all his subjects. The final major influence on Reiss’s style came in 1921, when, taking his eight-year-old son with him, he made his only return trip to Germany, where he visited his mother and sister. From September to the following May, Reiss traveled through Holland, Germany, Switzerland, Sweden, and Czechoslovakia. In Oberammergau, he made nineteen portraits of actors in the passion plays. In Sweden, he sketched country people; and in Germany, returning to his paternal roots, he drew thirty-eight Black Forest residents. As importantly, he visited Munich and Berlin and saw the work of the Neue Sachlichkeit (New Objectivity) artists, whose fidelity to life as it is seen and to the social conditions of the people confirmed him in his own objectivity. Stewart (p. 44) suggests that Reiss was also influenced by seeing the work of Max Beckmann (he later had a 1924 Beckmann monograph in his personal library). When Reiss returned to America he produced a series of “imaginatives,”composite images of New York (and sometimes specifically Harlem) nightlife that recall Beckmann’s style. Reiss’s work, however, steered clear of the anger and direct political engagement of the German artists. He found positive energy in his city scenes and high spiritual values in his pre-industrial, pre-capitalist peasants.
One of the most notable aspects of Reiss’s modernism, and a point on which he emphatically parted ways from artists who prized unintelligibility as proof of aesthetic virtue, was that for Reiss his art could only be successful insofar as it found patrons to support it and a public to understand it. Reiss’s modern interiors were cheerful and welcoming; his portraits of marginalized populations—native Americans, Mexican peasants, and Negroes of the Harlem Renaissance as well as the offshore Georgia Sea Islands— invariably expressed the theme of a commonly shared human dignity.
In New York, Reiss managed twin pursuits, becoming an influential teacher while maintaining a separate studio practice for his own work. He designed many well-known and well-loved commercial interiors, including, notably the chain of Longchamps restaurants in New York City and the splendid ballroom of the Hotel St. George in Brooklyn Heights. His Indian portrait work became part of the national visual culture when he acquired as a patron, Louis Hill, the owner of the Great Northern Railroad. In 1927, Hill purchased Reiss’s entire summer’s work, fifty-two portraits of American Indians. The relationship with the railroad proved long lasting and multi-faceted. The Great Northern used Reiss’s Indian portraits to illustrate months in its annual promotional calendars. Reiss’s designs also adorned the railroad’s menus, posters, and other promotional materials. Meanwhile he exhibited his work at the National Academy of Design, the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts, and the Los Angeles Museum. In 1933, Reiss completed his designs for murals in the Cincinnati Union (Railroad) Terminal. These murals, threatened with destruction in 1972, were saved after a public hue and cry. Some remain in the former railroad station, now a cultural center, while others have been reinstalled at the Greater Cincinnati-Northern Kentucky International Airport, where they remain highly prized.
The present set of two oil paintings were part of a nine-part mural design commissioned by Henry Lustig for the interior of a Longchamps Restaurant that opened in 1936 at 1450 Broadway, in New York, one block south of Times Square. The back story of Longchamps colorful and fascinating. Henry Lustig had begun in business peddling fruit on New York’s Lower East Side. He advanced to the wholesale produce business and on the way married Edith Rothstein, sister of Arnold Rothstein. Rothstein, from a highly respected and well off family, was, from childhood, an inveterate gambler, a passion that led him to a career as the acknowledged head of a far flung network of illegal activities which he fashioned into an empire of organized crime as well as legitimate businesses. In 1919, Rothstein arranged for his brother-in-law, Lustig, to open the first Longchamps Restaurant on a property Rothstein owned at 78th Street and Madison Avenue. Lustig, also a gambler who owned racehorses, named his premises after the famous racecourse outside of Paris. Rothstein was murdered in 1926, though he and Lustig likely fell out before that. (Truth is hard to separate from myth in discussions of Rothstein. Called “the Brain,” he is widely understood to have been the model for Meyer Wolfsheim in The Great Gatsby, as well as the model for characters in The Godfather and HBO’s Boardwalk.)
With the end of Prohibition in December 1933, Lustig opened a series of Longchamps restaurants at high profile locations around Manhattan. The restaurants were intended to be elegant, serving sophisticated food and drink in glamourous surroundings to a reliable crowd of “regulars” who had money, but also accessible to middle class patrons looking for celebratory meals. Lustig hired top architects, Louis Alan Abramson and Ely Jacques Kahn. In fact, Kahn had designed 1450 Broadway, a 42-story office building called “The Continental” that opened in 1931 (and remains to this day). These were the years of the Great Depression and Lustig was commissioning interiors for patrons who wanted to wine and dine in settings worthy of a Busby Berkeley film.
For his interiors, Henry Lustig turned to Winold Reiss. Reiss already boasted a portfolio ready made for Lustig’s purposes. Through his shipmate friend of 1913, Alfons L. Baumgarten, Reiss had connected with Baumgarten’s brother Otto, already in New York and intent on going into the restaurant business. Baumgarten’s father owned a restaurant in Vienna and, in 1919, Reiss served as the designer for Baumgarten’s Restaurant Crillon. The commission attracted favorable notice and Reiss went on to design interiors and packaging for Baumgarten’s Café Viennois and for his candy business, Baumgarten Viennese Bonbonniѐre. In 1923, Reiss decorated rooms and hallways and designed interiors and murals for the restaurant and night club at the top of the Hotel Alamac, a new 19-story hotel at 71st Street and Broadway that advertised itself as “three minutes from Times Square,” a reference to its location one express subway stop...
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Canvas, Oil
City of the Future, Panel II
By Winold Reiss
Located in New York, NY
French modern art made a dramatic entrance into on America in 1913 at the famous Armory Show in New York City. In that same year, German twentieth-century art also arrived, with no fanfare, in the person of Winold Reiss, who disembarked from the S. S. Imperator on October 29, 1913, at Ellis Island in New York harbor. (The most accessible discussion of Reiss remains Jeffrey C. Stewart, To Color America: Portraits by Winold Reiss, exhib. cat. [Washington, D.C.: National Portrait Gallery, Smithsonian Institution, 1989]. A very useful overview of Reiss’s career is contained in “Queen City Heritage: Cincinnati Union Terminal and the Artistry of Winold Reiss,” The Journal of the Cincinnati Historical Society 51 [Summer/Fall 1993]). Reiss was already twenty-seven years old when he came to America, thoroughly educated in a rigorous and inclusive heritage of German art that reflected decades of central European modernism.
Reiss’s father, Fritz Reiss (1857–1914), had trained as a landscape painter and portraitist at the renowned academy in Düsseldorf. Working as an illustrator, and proficient in watercolor as well as oil, Fritz Reiss moved his family, in the 1899, to Freiburg, a small village in southwest Germany near the Black Forest, so that he could paint honest portraits of local peasants. This choice reflected a prevailing spirit of romantic nationalism in the fine arts, architecture, and literature that was expressed in arts and crafts movements across Europe. Two of Fritz Reiss’s sons followed their father into art. Hans became a sculptor, immigrated to Sweden, and eventually joined his brother in America. Winold’s first art teacher was his father. In 1911, Reiss went to Munich where he studied with Franz von Stuck at the Academy of Fine Arts and with Julius Diez at the School of Applied Arts. Von Stuck was an influential art nouveau artist, designer, sculptor, and architect whose graphic style tended toward imaginative symbolism. Diez was master of mural painting who gained renown for his commercial poster designs executed in the Jugendstil manner. While Reiss absorbed stylistic influences from both of these men, perhaps the most lasting lesson was the freedom with which German fine artists crossed genres, working in the fine arts and the applied arts as circumstances warranted, without prejudice to their standing in either field. This permeable boundary, a characteristic of German arts and crafts practice, was also championed by John Ruskin and William Morris, in England. While his European versatility enabled Reiss to support his family in America, it ultimately hampered his full acceptance as a fine artist.
Reiss was proficient in graphics, fabric design, interior decoration, mural and poster art, as well as landscape and portrait painting. When he first arrived in America he established himself across a broad range of these interests, working in illustration, poster design, interior decoration, and as a teacher. His first major interior commission, the Busy Lady Bakery in New York City (Stewart, p. 30 illus.), strongly recalls the design work a decade earlier of Josef Hoffman in Vienna and Charles Rennie Mackintosh in Glasgow. While fellow German immigrants were among Reiss’s first commercial patrons, by 1915 he had been invited to lecture on the German poster at the Art Students League in New York. Anti-German feeling accompanying America’s entry into World War I derailed some of Reiss’s projects, but still, in 1914 and 1915, he designed covers for Scribner’s magazine.
None of this, however, was what had drawn Reiss to America. The story goes that he came to America to live out his childhood fantasies. Like many other German boys, Reiss had been captivated in his youth by tales of the American “wild west” widely circulated in the imaginative fiction of the German author Karl May. Reiss had also read, in translation, the works of James Fennimore Cooper. Numerous explanations can be put forth to explain Reiss’s emigration to America in 1913. The combined reasons must have been compelling enough to leave behind a pregnant wife (she and his son, Tjark, born in December 1913, joined him in America in 1914). These reasons included, no doubt, the war clouds over Europe, the increasing militarism of German society (Reiss’s brother Hans, was a pacifist) and the large number of artists already working in Germany. Still, for Reiss, America meant the Indian.
In January 1920, Reiss realized his dream of traveling west to Indian country. He went with a student to the Blackfoot Reservation in Browning, Montana. Thus began a relationship with Native Americans that lasted all of his life. Reiss produced thirty-six portraits of Blackfoot Indians in the winter of 1920. When he exhibited these in New York in 1920, at the E. F. Hanfstaengl Galleries, they were purchased as a group by Dr. Philip Cole, a native of Montana. In October 1920, Reiss made a sketching trip to Mexico, painting portraits and landscapes. As he traveled, Reiss’s style began to reflect the influence of the aesthetics, color palette, and patterns of indigenous American visual culture. He blended this into his now hyphenated German-American vocabulary, reaching for an artistic language expressed in the most universally accessible terms that would convey the respect he felt for all his subjects. The final major influence on Reiss’s style came in 1921, when, taking his eight-year-old son with him, he made his only return trip to Germany, where he visited his mother and sister. From September to the following May, Reiss traveled through Holland, Germany, Switzerland, Sweden, and Czechoslovakia. In Oberammergau, he made nineteen portraits of actors in the passion plays. In Sweden, he sketched country people; and in Germany, returning to his paternal roots, he drew thirty-eight Black Forest residents. As importantly, he visited Munich and Berlin and saw the work of the Neue Sachlichkeit (New Objectivity) artists, whose fidelity to life as it is seen and to the social conditions of the people confirmed him in his own objectivity. Stewart (p. 44) suggests that Reiss was also influenced by seeing the work of Max Beckmann (he later had a 1924 Beckmann monograph in his personal library). When Reiss returned to America he produced a series of “imaginatives,”composite images of New York (and sometimes specifically Harlem) nightlife that recall Beckmann’s style. Reiss’s work, however, steered clear of the anger and direct political engagement of the German artists. He found positive energy in his city scenes and high spiritual values in his pre-industrial, pre-capitalist peasants.
One of the most notable aspects of Reiss’s modernism, and a point on which he emphatically parted ways from artists who prized unintelligibility as proof of aesthetic virtue, was that for Reiss his art could only be successful insofar as it found patrons to support it and a public to understand it. Reiss’s modern interiors were cheerful and welcoming; his portraits of marginalized populations—native Americans, Mexican peasants, and Negroes of the Harlem Renaissance as well as the offshore Georgia Sea Islands— invariably expressed the theme of a commonly shared human dignity.
In New York, Reiss managed twin pursuits, becoming an influential teacher while maintaining a separate studio practice for his own work. He designed many well-known and well-loved commercial interiors, including, notably the chain of Longchamps restaurants in New York City and the splendid ballroom of the Hotel St. George in Brooklyn Heights. His Indian portrait work became part of the national visual culture when he acquired as a patron, Louis Hill, the owner of the Great Northern Railroad. In 1927, Hill purchased Reiss’s entire summer’s work, fifty-two portraits of American Indians. The relationship with the railroad proved long lasting and multi-faceted. The Great Northern used Reiss’s Indian portraits to illustrate months in its annual promotional calendars. Reiss’s designs also adorned the railroad’s menus, posters, and other promotional materials. Meanwhile he exhibited his work at the National Academy of Design, the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts, and the Los Angeles Museum. In 1933, Reiss completed his designs for murals in the Cincinnati Union (Railroad) Terminal. These murals, threatened with destruction in 1972, were saved after a public hue and cry. Some remain in the former railroad station, now a cultural center, while others have been reinstalled at the Greater Cincinnati-Northern Kentucky International Airport, where they remain highly prized.
The present set of two oil paintings were part of a nine-part mural design commissioned by Henry Lustig for the interior of a Longchamps Restaurant that opened in 1936 at 1450 Broadway, in New York, one block south of Times Square. The back story of Longchamps colorful and fascinating. Henry Lustig had begun in business peddling fruit on New York’s Lower East Side. He advanced to the wholesale produce business and on the way married Edith Rothstein, sister of Arnold Rothstein. Rothstein, from a highly respected and well off family, was, from childhood, an inveterate gambler, a passion that led him to a career as the acknowledged head of a far flung network of illegal activities which he fashioned into an empire of organized crime as well as legitimate businesses. In 1919, Rothstein arranged for his brother-in-law, Lustig, to open the first Longchamps Restaurant on a property Rothstein owned at 78th Street and Madison Avenue. Lustig, also a gambler who owned racehorses, named his premises after the famous racecourse outside of Paris. Rothstein was murdered in 1926, though he and Lustig likely fell out before that. (Truth is hard to separate from myth in discussions of Rothstein. Called “the Brain,” he is widely understood to have been the model for Meyer Wolfsheim in The Great Gatsby, as well as the model for characters in The Godfather and HBO’s Boardwalk.)
With the end of Prohibition in December 1933, Lustig opened a series of Longchamps restaurants at high profile locations around Manhattan. The restaurants were intended to be elegant, serving sophisticated food and drink in glamourous surroundings to a reliable crowd of “regulars” who had money, but also accessible to middle class patrons looking for celebratory meals. Lustig hired top architects, Louis Alan Abramson and Ely Jacques Kahn. In fact, Kahn had designed 1450 Broadway, a 42-story office building called “The Continental” that opened in 1931 (and remains to this day). These were the years of the Great Depression and Lustig was commissioning interiors for patrons who wanted to wine and dine in settings worthy of a Busby Berkeley film.
For his interiors, Henry Lustig turned to Winold Reiss. Reiss already boasted a portfolio ready made for Lustig’s purposes. Through his shipmate friend of 1913, Alfons L. Baumgarten, Reiss had connected with Baumgarten’s brother Otto, already in New York and intent on going into the restaurant business. Baumgarten’s father owned a restaurant in Vienna and, in 1919, Reiss served as the designer for Baumgarten’s Restaurant Crillon. The commission attracted favorable notice and Reiss went on to design interiors and packaging for Baumgarten’s Café Viennois and for his candy business, Baumgarten Viennese Bonbonniѐre. In 1923, Reiss decorated rooms and hallways and designed interiors and murals for the restaurant and night club at the top of the Hotel Alamac, a new 19-story hotel at 71st Street and Broadway that advertised itself as “three minutes from Times Square,” a reference to its location one express subway stop...
Category
20th Century American Modern Winold Reiss Art
Materials
Canvas, Oil
Winold Reiss art for sale on 1stDibs.
Find a wide variety of authentic Winold Reiss art available for sale on 1stDibs. If you’re browsing the collection of art to introduce a pop of color in a neutral corner of your living room or bedroom, you can find work that includes elements of orange and other colors. You can also browse by medium to find art by Winold Reiss in crayon, ink, pastel and more. Much of the original work by this artist or collective was created during the 20th century and is mostly associated with the modern style. Not every interior allows for large Winold Reiss art, so small editions measuring 12 inches across are available. Customers who are interested in this artist might also find the work of Emil Bisttram, Jan Matulka, and Stuart Davis. Winold Reiss art prices can differ depending upon medium, time period and other attributes. On 1stDibs, the price for these items starts at $1,900 and tops out at $22,000, while the average work can sell for $6,950.