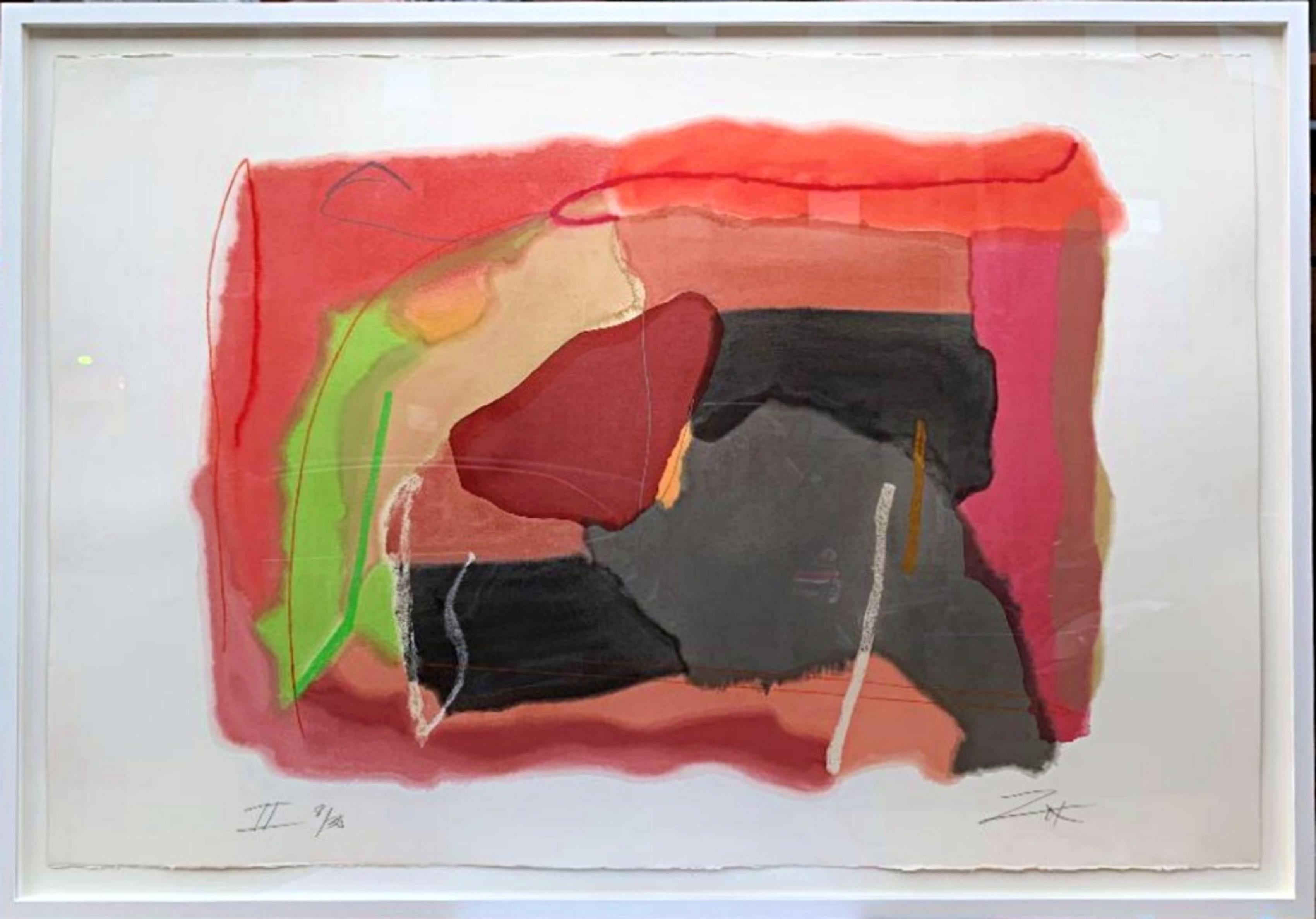
Larry Zox
Dexter's Choice, State II, ca. 1990
Mixed media, Watercolor pochoir, and Oil stick Wax, Water-Based Crayons, on heavy Arches museum watercolor rag paper with deckled edges
40 × 60 in
101.6 × 152.4 cm
Edition 8/30 (unique variant)
Frame included
Measurements:
Sheet: 40 inches (vertical) by 60 inches (horizontal)
Frame: 42 inches x 62 inches x 1 inch
Dexter's Choice, State # II is a unique, mixed media work from an edition of 30 unique variants done in pochoir, (25 stencils, 14 colors). Here, Zox uses watercolor instead of inks, which is applied to heavy 300 lb. watercolor paper. Although it is a multiple signed and numbered from the edition of 30, each work of art is unique because of how the paper receives the watercolor brush. In addition, this work is created like a mixed media painting because it has 11 lines added by hand with wax and water based crayons and oil sticks. The unique watercolor technique that Zox employed in making "Dexter's Choice" is documented in the textbook, "Screen Printing: Water Based Techniques,Roni Henning, NYIT ".
Dexter's Choice was published by Images Gallery, and this work was acquired directly from the publisher before they sold out. This work is elegantly floated and framed in a white wood frame.
Accompanied by gallery issued Certificate of Guarantee
Larry Zox Biography:
A PAINTER who played an essential role in the Color Field discourse of the 1960s and 1970s, Larry Zox is best known for his intensely and brilliantly colored geometric abstractions that question and violate symmetry.1 Zox stated in 1965: “Being contrary is the only way I can get at anything.” To Zox, this position was not necessarily arbitrary, but instead meant “responding to something in an examination of it [such as] using
a mechanical format with X number of possibilities.”2 What he sought was to “get at the specific character and quality of each painting in and for itself,” as James Monte stated in his introductory essay in the catalogue for Zox’s 1973–1974 solo exhibition at the Whitney Museum of American Art.3 Zox’s robust paintings reveal
a celebrated artist and master of composition who is explored and challenged the possibilities of Post-Painterly Abstraction and Minimalist pictorial conventions.
Zox began to receive attention in the 1960s when he was included in several groundbreaking exhibitions of Color Field and Minimalist art, including Shape and Structure (1965), organized by Henry Geldzahler and Frank Stella for Tibor de Nagy, New York, and Systemic Painting (1966), organized by Lawrence Alloway for the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, New York. In 1973–1974, the Whitney’s solo exhibition of Zox’s work gave recognition to his significance in the art scene of the preceding decade. In the following year, he was represented in the inaugural exhibition of the Hirshhorn Museum and Sculpture Garden, Wahsington, DC, which acquired fourteen of his works.
Zox was born in Des Moines, Iowa in 1937. He attended the University of Oklahoma and Drake University, Des Moines, Iowa, and then studied under George Grosz at the Des Moines Art Center. In 1958, Zox moved to New York, joining the downtown art scene. His studio on 20th Street became a gathering place for artists, jazz musicians, bikers, and boxers, and he occasionally sparred with visiting fighters. He later established a studio in East Hampton, a former black smithy used previously by Jackson Pollock.
In his earliest works, such as Banner (1962) Zox created
collages consisting of pieces of painted paper stapled onto sheets of plywood. He then produced paintings that were illusions of collages, including both torn- and trued-edged forms, to which he added a wide range of strong hues that created ambiguous surfaces. In paintings such as For Jean (1963), he omitted the collage aspect of his work and applied flat color areas to create more complete statements of pure color and shape. He then replaced these torn and expressive edges with clean and impersonal lines that would define his work for the next decade.
From 1962 to 1965, he produced his Rotation series, at first creating plywood and Plexiglas reliefs, which turned squares into dynamic polygons. He used these shapes in his paintings as well, employing white as a foil between colors to produce negative spaces that suggest that the colored shapes had only been cut out and laid down instead of painted. The New York Times in 1964 wrote of the works in show such as Rotation B (1964) and of the artist: “The artist is hip, cool, adventurous, not content to stay with the mere exercise of sensibility that one sees in smaller works.”4
In 1965, he began the Scissor Jack series, in which he arranged opposing triangular shapes with inverted Vs of bare canvas at their centers that threaten to split their compositions apart. In several works from this series, Zox was inspired by ancient Chinese water vessels. With a mathematical precision and a poetic license, Zox flattened the three dimensional object onto graph paper, and later translated his interpretation of the vessel’s lines onto canvas with masking tape, forming the structure of the painting.
The Diamond Cut and Diamond
Drill paintings...